Fri, Feb 6, 2026
[Archive]
Abstract: (661 Views)
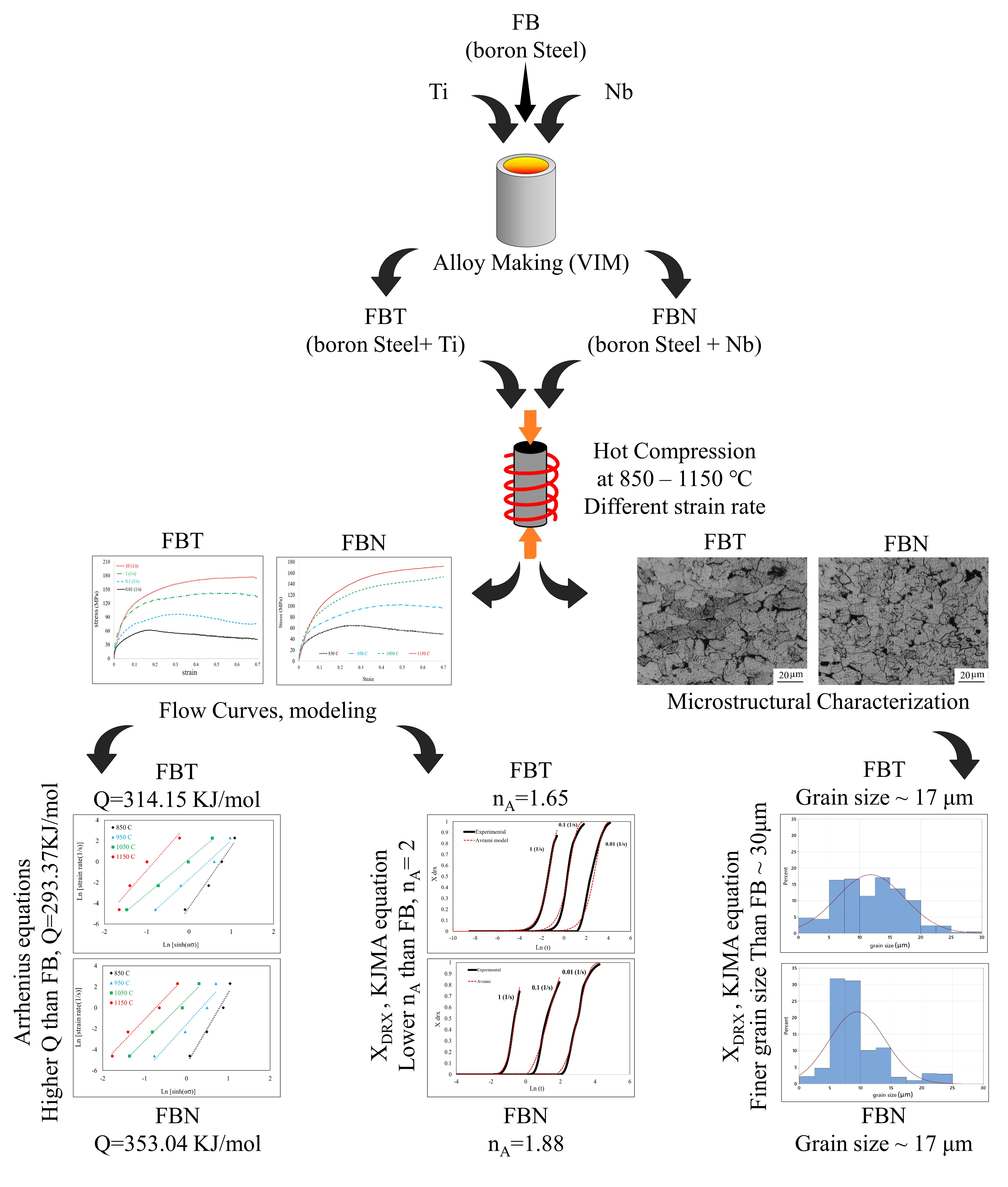
The hot deformation behavior modeling and microstructural evolution of low-carbon boron steels with Ti (FBT) and Nb (FBN) additions were investigated and compared with a baseline boron-treated steel (FB) in our previous work. Hot compression tests were conducted at temperatures of 850–1150 °C and strain rates of 0.01–10 s⁻¹. Flow curve analysis revealed that both Ti and Nb increased flow stress and delayed the onset of dynamic recrystallization (DRX), with the effect more pronounced in FBN. Constitutive analysis based on the Arrhenius model showed that the activation energy of deformation increased from 293.37 kJ/mol in FB to 314.15 kJ/mol in FBT and 353.04 kJ/mol in FBN, highlighting the strong pinning effect of precipitates. Critical stresses and strains (σc, σp, εc, εp) followed the order FB < FBT < FBN, indicating higher resistance to recrystallization in the microalloyed steels. DRX kinetics, modeled using the Avrami equation, yielded exponents of 2.09, 1.65, and 1.88 for FB, FBT, and FBN, respectively, confirming that Ti suppressed nucleation more strongly than Nb. Microstructural analysis demonstrated that Ti inhibited BN formation and promoted TiN/Ti(C,N), whereas Nb retained BN and generated Nb(C,N), mainly at MnS interfaces. Grain size distribution analysis revealed that both FBT and FBN exhibited significantly finer and more homogeneous grains compared to FB, with average grain sizes at 1150 °C (0.1 s⁻¹) of 17.3 μm in FBT and 17.0 μm in FBN, nearly half that of FB (33.6 μm). Overall, Ti and Nb additions distinctly altered the high-temperature deformation and recrystallization mechanisms of boron steels, enhancing grain refinement while suppressing DRX, thereby extending the findings of our previous study on FB.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Materials Modeling and Simulation
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |