Thu, Dec 26, 2024
[Archive]
Volume 20, Issue 2 (June 2023)
IJMSE 2023, 20(2): 1-14 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Hooshyar M, Torshabi M, Kazemi M. Acceleration of Bone-Implant Graft by Optimizing the Dimention and Crystalline Structure of Titanium, Oxide Nanotubes as the Titanium-Based Implant Coating. IJMSE 2023; 20 (2) :1-14
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-2925-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-2925-en.html
Abstract: (8022 Views)
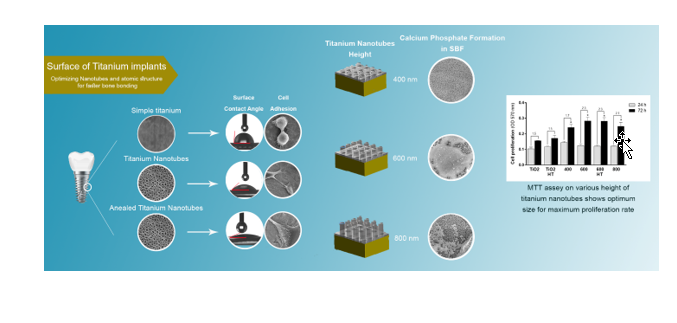
Titanium implants are one of the most durable and conventional orthopedic and dental implants. The goal of this research is to improve the bio-compatibility of these implants by implementing nano coating of titanium oxide nanotubes (TNT) to enhance bone graft on the implant surface, and reduction of wound healing duration and risk of implant surgery at the same time. For this purpose, the effects of dimension and atomic structure of titanium oxide nanotubes are examined on the surface properties and biological performance and tried to introduce an optimum status of this nano-tubular structure. TNTs were synthesized by anodizing method on the surface of titanium sheets. Dimensions of TNT can be controlled by anodizing process parameters. Heat treatment affects the atomic structure of TNTs. Contact angle measurement as one of the important surface properties was investigated on different dimensions and structures of TNTs, to study human blood's physical interaction with the implant surface. In addition, the quality and quantity of bone material sediment on the surface were examined by SBF test and SEM analysis. Finally, cell culture provided informative data on bone cells' response to these nanotubular coatings by analyzing MTT results and SEM photography of cells. As a result, the optimum dimension and atomic structure of TNTs were defined and the required process parameters were introduced to obtain this state. This setup can be used as an optimum state of TNT as a nano coating on titanium implant with orthopedic functions to enhance the cell adhesion and acquire the highest proliferation rate which means faster bone graft and shorter convalescence.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Coatings and Corrosion Phenomenon
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |